-
Home / AMSS Events / All News
A data integration approach unveils a transcriptional signature of type 2 diabetes progression in rat and human islets
 Watch Video
Watch Video
10 17, 2023
Type 2 diabetes (T2D) is a complex, chronic, progressive, and non-self-curable disease, whose cure is a challenge to public health. China now has more than 100 million T2D patients, along with an even larger population of prediabetes. Unfortunately, a substantial portion of these individuals remains unaware of their risk and status. Detecting diabetes early before it becomes irreversible is a desirable approach to cure the disease.
An integration of large expression data from rat and human islets published in PLOS ONE on October 10, 2023 supported a new scheme of detecting prediabetes. That is, screening for prediabetes should include fasting and postprandial blood insulin levels along with glucose levels; Moreover, to prevent the islet morphological alteration from becoming irreversible, or to prevent T2D pathological progression from irreversible, active intervention should be taken at as early as the stage of hyperinsulinemia even with euglycemia.
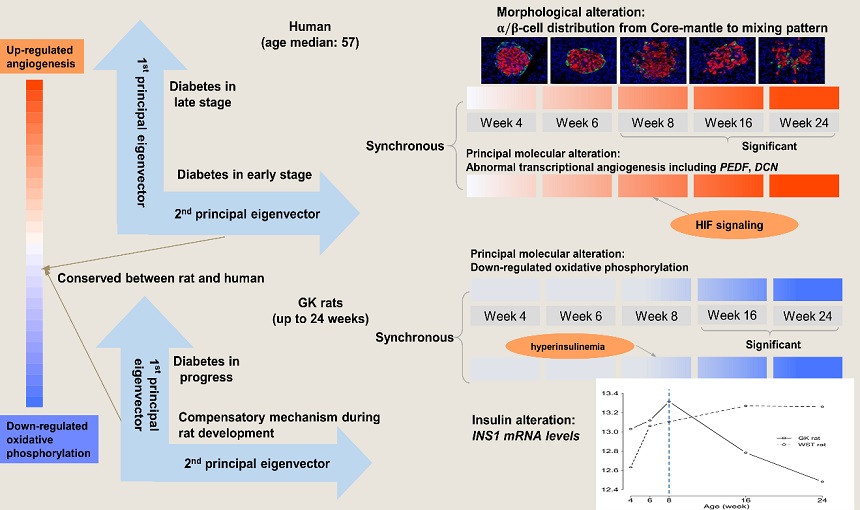
Pancreatic islet failure is a key characteristic of T2D besides insulin resistance. The research group led by Dr. Lei M Li at Academy of Mathematics and Systems Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences, discovered that irreversible islet deterioration coincides with transcriptional angiogenesis and hyperinsulinemia precedes the onset of insulin deterioration. They unveiled the findings by developing a novel computational approach to integrating expression profiles of Goto-Kakizaki (GK) and Wistar (WST) rat islets from a designed experiment with those of the human islets from an observational study.
The GK rat is an T2D animal model, displaying both impaired insulin secretion in response to glucose and insulin resistance, while the WST rat serves as its control counterpart. In islets, α and β cells respectively produce and secret the two hormones: glucagon and insulin. Glucagon raises glucose levels whereas insulin is the sole hormone responsible for reducing plasma glucose levels. Other than expression profiles, the α/β-cell distribution is available in GK/WST rat islets. The human islets were from cadaver donors including non-diabetics and diabetics. The information such as age, gender, BMI, and HbA1c levels are available along with the mRNA expressions. All data utilized in this research was from public repository at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/. The rat data were generated by Chinese Academy of Sciences, and the human data were from Nordic Islet Transplantation Programme.
The integration analysis is based on the dual eigen-structure of the expression profiles. The principal gene eigenvector or signature, which was characterized by up-regulated angiogenesis and down-regulated oxidative phosphorylation, was identified conserved across the two species. In the case of GK versus WST islets, such alteration in gene expression can be verified directly by the treatment-control tests at various time points throughout the study. The alteration of transcriptional angiogenesis, which was synchronous to that of the α/β-cell distribution, preceded the down-regulation of oxidative phosphorylation, which was synchronous to the insulin deterioration. Moreover, hyperinsulinemia was observed before the onset of insulin deterioration in GK rats.
According to the expression signature, a large portion of genes involved in the hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) signaling pathway, which activates the transcription of angiogenesis, were markedly up-regulated. The findings from the research suggest that along the T2D progression, the HIF signaling pathway functions under hypoxic stress. Furthermore, the presence of the top-ranked anti-angiogenic genes THBS1 and PEDF indicate the existence of a counteractive mechanism that is in line with thickened and fragmented capillaries found in the deteriorated islets.
In addition to the public raw data, the computational code and intermediate data have been deposited on open cloud platforms https://codeocean.com and https://zenodo.org so that all the results presented in the article are reproducible.
 Contacts:
Contacts:
 E-mail:
E-mail:

Copyright@2008,All Rights Reserved, Academy of Mathematics and Systems Science,CAS
Tel:86-10-82541777 Fax: 86-10-82541972 E-mail: contact@amss.ac.cn
京ICP备05002806-1号 京公网安备110402500020号